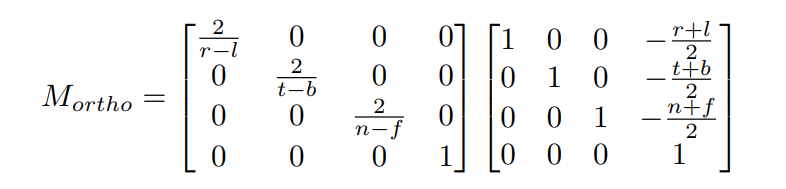1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
|
// 基于摄像机类,使用MVP矩阵转换
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <Shader.h>
#include <Camera.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/type_ptr.hpp>
// 定义屏幕属性
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
// 摄像机
Camera camera(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 3.0f));
float lastX = SCR_WIDTH / 2.0f;
float lastY = SCR_HEIGHT / 2.0f;
bool firstMouse = true;
// 时间
float deltaTime = 0.0f; // 当前帧与上一帧的时间差
float lastFrame = 0.0f;
// 定义回调函数
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window, Shader& ourShader);
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos);
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset);
int main() {
glfwInit();
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL) {
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress)) {
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
glViewport(0, 0, SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
glfwSetCursorPosCallback(window, mouse_callback);
glfwSetScrollCallback(window, scroll_callback);
// 创建并编译渲染器
Shader ourShader("E:/OpenGL Project/Project1/shaders/3.3.shader.vs",
"E:/OpenGL Project/Project1/shaders/3.3.shader.fs");
float vertices[] = {
// ---- 位置 ---- - 纹理坐标 -
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
-0.5f, 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f
};
// 立方体在世界空间的位置
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f)
};
// 定义顶点缓冲、顶点数组
unsigned int VBO, VAO;
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
// 绑定VAO
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
// 把顶点数组复制到缓冲中供OpenGL使用
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// 设置顶点位置
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// 设置顶点纹理坐标
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
unsigned int texture1, texture2;
// 创建纹理1
glGenTextures(1, &texture1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
// 为当前绑定的纹理对象设置环绕、过滤方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// 加载并生成纹理
int width, height, nrChannels;
unsigned char* data = stbi_load("container.jpg", &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
// 纹理及多级渐远纹理生成完毕后,释放图片内存
stbi_image_free(data);
// 创建纹理2
glGenTextures(1, &texture2);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
stbi_set_flip_vertically_on_load(true); // 读取图片时翻转图片的y轴用于解决OpenGL与图片y轴坐标相反的情况
data = stbi_load("awesomeface.png", &width, &height, &nrChannels, 0);
if (data)
{
// 请注意,awesomeface.png具有透明度,因此有一个alpha通道,所以请确保告诉OpenGL数据类型是GL_RGBA
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, width, height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
}
else
{
std::cout << "Failed to load texture" << std::endl;
}
stbi_image_free(data);
ourShader.use(); // 不要忘记在设置uniform变量之前激活着色器程序!
ourShader.setInt("texture1", 0);
ourShader.setInt("texture2", 1);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); // 开启Z-Buffer,默认情况下OpenGL关闭了Z-Buffer
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED); // 隐藏鼠标
// 渲染循环
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// 每帧时间逻辑
float currentFrame = glfwGetTime();
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame;
lastFrame = currentFrame;
// 输入
processInput(window, ourShader);
// 清屏
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); // 清理颜色缓冲值和深度缓冲值
// 激活并绑定材质
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture1);
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE1);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture2);
// 激活渲染器
ourShader.use();
// 坐标变换
glm::mat4 projection = glm::mat4(1.0f);
projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(camera.Zoom), (float)SCR_WIDTH/ (float)SCR_HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
ourShader.setMat4("projection", projection);
glm::mat4 view = camera.GetViewMatrix();
ourShader.setMat4("view", view);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
glm::mat4 model(1.0f);
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
float angle = 20.0f * i;
if (i % 3 == 0) {
angle = glfwGetTime() * 25.0f;
}
model = glm::rotate(model, glm::radians(angle), glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));
ourShader.setMat4("model", model);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 36);
}
// 检查并调用事件,交换缓冲
glfwPollEvents();
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// 视口回调函数
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height) {
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}
// 键盘输入回调函数
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window, Shader& ourShader)
{
static float percentage = 0.2f;
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_UP) == GLFW_PRESS) {
percentage += 0.01f;
percentage = std::min(percentage, 1.0f);
}
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_DOWN) == GLFW_PRESS) {
percentage -= 0.01f;
percentage = std::max(percentage, 0.0f);
}
ourShader.setFloat("percentage", percentage);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_W) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(FORWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_S) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(BACKWARD, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_A) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(LEFT, deltaTime);
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_D) == GLFW_PRESS)
camera.ProcessKeyboard(RIGHT, deltaTime);
}
// 鼠标回调函数
void mouse_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xpos, double ypos)
{
if (firstMouse)
{
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
firstMouse = false;
}
float xoffset = xpos - lastX;
float yoffset = lastY - ypos; // reversed since y-coordinates go from bottom to top
lastX = xpos;
lastY = ypos;
camera.ProcessMouseMovement(xoffset, yoffset);
}
// 鼠标滚轮回调函数
void scroll_callback(GLFWwindow* window, double xoffset, double yoffset)
{
camera.ProcessMouseScroll(yoffset);
}
|